Recognizing a ventral septal defect in children early is vital for their well-being. Symptoms can be subtle yet impactful. Knowing these signs ensures better healthcare. This blog guides you in spotting them and emphasizes the importance of consulting medical professionals to ensure timely intervention and care for affected children.
Introduction to Ventral Septal Defect
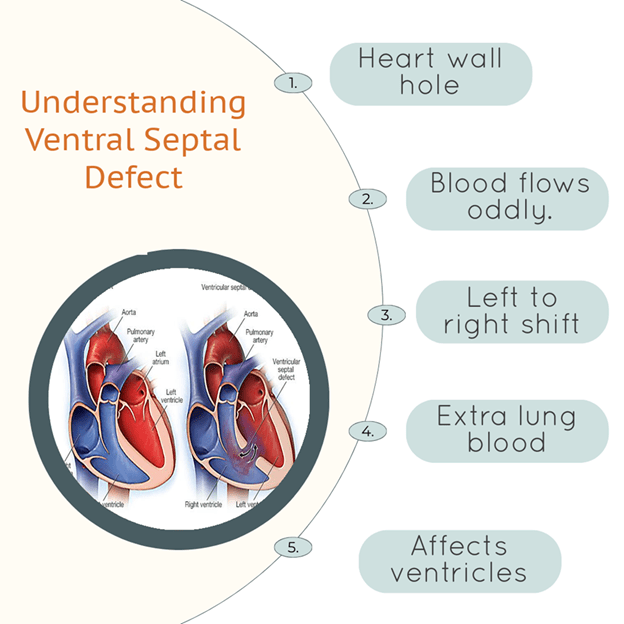
A ventral septal defect (VSD) is a hole in the heart’s wall, affecting how blood flows. This defect occurs between the heart’s lower chambers, called ventricles. Due to this hole, blood flows from the left to the right side of the heart, causing extra blood to be pumped into the lungs.
Spotting VSD early can help manage any complications effectively. Early detection also ensures appropriate ventral septal defect treatment options can be considered. This blog will explore signs, diagnosis, and treatment pathways, providing insight into living with VSD. Understanding these aspects is beneficial for caregivers and parents aiming to offer the best care.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Heart
The heart is a crucial organ comprising four main chambers. These are the right and left atria at the top, and right and left ventricles at the bottom. The ventricles are separated by a wall, crucial for maintaining proper blood flow.
A ventral septal defect creates a hole in this wall, leading to improper blood flow between the lower chambers. This condition can range from small to large defects, influencing the symptoms experienced. The size of the defect can determine the heart’s workload and symptom severity.
- Small Defects: These may close naturally and might not show symptoms. However, regular monitoring is needed.
- Moderate to Large Defects: They may cause symptoms and require medical intervention, like surgery or medication.
Understanding the structure of the heart and the impact of ventral septal defect treatment is crucial for recognizing potential signs and planning effective care.
Recognizing Signs and Symptoms
Spotting a ventral septal defect in children involves observing common symptoms:
- Heart Murmurs: An unusual sound heard during a heartbeat.
- Rapid Breathing: Especially during feeding in infants.
- Poor Feeding and Weight Gain: Taking longer to feed and not meeting growth milestones.
The severity and size of the defect often determine symptom intensity. Larger defects usually result in more noticeable signs, such as excessive sweating or noticeable fatigue during activities. Recognizing these early can lead to timely and effective treatment.
Role of Regular Pediatric Check-Ups
Regular pediatric check-ups are essential for detecting a ventral septal defect early. These visits help monitor a child’s growth and development, providing clues about heart health.
Pediatricians can detect heart murmurs and other symptoms that might not be evident at home. As experts, their skills in monitoring and measuring growth help highlight any abnormalities requiring further investigation. These routine visits ensure early ventral septal defect treatment options are explored, preventing more severe health issues later.
When to Seek Medical Advice?
Certain symptoms in a child may require immediate medical advice:
- Difficulty Eating or Breathing: Especially in young babies.
- Blueness or Cyanosis: Signs of poor oxygen levels.
- Constantly Tired: Especially if unusual for their age and activity.
While routine signs like mild heart murmurs necessitate a pediatric consultation, urgent symptoms like those above need immediate medical attention. It’s crucial for parents to trust their instincts. If something feels off, seek medical advice to ensure the child’s well-being.
Diagnosis and Evaluation Methods
Diagnosing a ventral septal defect involves several tools. Pediatricians may use:
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound imaging for the heart.
- Physical Exams: Listening to the heart sounds.
- Chest X-rays and MRIs: To understand the heart’s size and function.
These tools help determine the size of the defect and plan the appropriate treatment. Understanding these methods ensures transparency in the process, allowing parents to make informed healthcare decisions.
Treatment Approaches for VSD
Ventral septal defect treatment varies depending on the defect’s size and symptoms. Here is an overview of common interventions at BlueBird Children’s Hospital:
- Monitoring: Small defects often require no treatment, just regular check-ups to see if the hole closes naturally.
- Medication: To reduce symptoms by managing blood pressure and heart function.
- Surgery: Used for moderate to large defects to repair the hole.
Pediatric heart surgery at BlueBird is innovative, with minimally invasive options being prioritized where possible. Advances in medical technology allow for effective, safer treatment for children with VSD, ensuring they can lead healthy lives.
Life with VSD: Guidance for Families
Supporting a child with a ventral septal defect involves several key actions:
- Maintain a nutritious diet to promote heart health.
- Ensure vaccinations are up-to-date to prevent illnesses.
- Regularly monitor for any new or worsening symptoms.
Understanding and following these guidelines help in maintaining the child’s quality of life and overall health. With proper care, children with VSD can enjoy active, fulfilling lives.
Conclusion and Useful Resources
Identifying and managing a ventral septal defect in children early offers more effective outcomes. Recognizing the common signs and trusting your instincts are vital steps. Regular pediatric visits help in early detection and effective ventral septal defect treatment.
For additional support, consider resources like the American Heart Association and the BlueBird Children’s Hospital, which provide invaluable information and assistance. By staying informed and proactive, parents can ensure their children with VSD receive the appropriate care needed to thrive.